Comparison and analysis of 4 kinds of filters
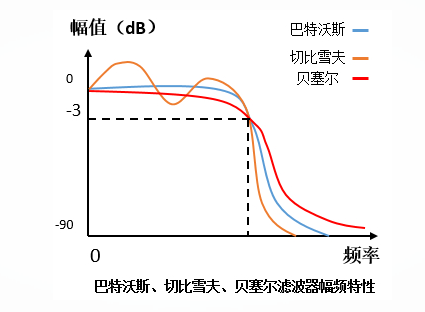
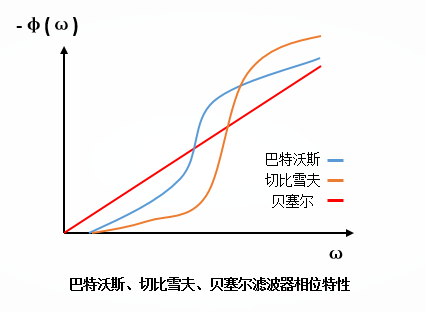
1. Digital filter Digital filter refers to a discrete-time linear time-invariant system implemented by a finite-precision algorithm that performs signal filtering processing. Its input is a set of digital variables, and its output is another set of converted digital variables. Therefore, it can be either a dedicated digital computer assembled with digital hardware to complete a given operation, or it can be a program for the required operation to be executed by a general-purpose computer. Digital filters have the advantages of high stability, high accuracy, and flexibility. With the development of digital technology, the use of digital technology to realize the function of filters has attracted more and more people's attention and wide application. 2. Butterworth filter The characteristic of Butterworth filter is that the frequency response curve in the pass band is as flat as possible, without fluctuations, and gradually decreases to zero in the stop band. On the Bode plot of the logarithmic diagonal frequency of the amplitude, starting from a certain boundary angular frequency, the amplitude gradually decreases with the increase of the angular frequency and tends to negative infinity. The frequency characteristic curve of Butterworth filter is a monotone function of frequency in both passband and stopband. Therefore, when the index requirements are met at the boundary of the passband, there must be a margin in the passband. Therefore, a more effective design method should be to evenly distribute the accuracy in the entire passband or stopband, or both. In this way, a lower order system can be used to meet the requirements. This can be achieved by choosing an approximation function with equal ripple characteristics. 3. Bessel filter The Bessel filter is a linear filter with maximum flat group delay (linear phase response). Bezier filters are commonly used in audio overpass systems. The analog Bezier filter is depicted as a constant group delay that spans almost the entire passband, thus maintaining the filtered signal waveform over the passband. Bessel filters have the flattest amplitude and phase response. The phase response of the bandpass (usually the user's area of ​​interest) is nearly linear. Bessel filters can be used to reduce the nonlinear phase distortion inherent in all IIR filters. 4. Chebyshev filter The Chebyshev filter is a filter that fluctuates in the frequency response amplitude and other ripples in the passband or stopband, and the amplitude characteristic is equal ripple in the passband. The monotonic in the stop band is called Chebyshev type I filter; the amplitude characteristic is monotonic in the pass band, and the equal ripple in the stop band is called Chebyshev type II filter. The form of Chebyshev filter used depends on the actual application. When the filters have the same order: Butterworth filter has the flattest pass band and slow stop band drop. Chebyshev filter passband and other ripples, the stopband drops faster. Bessel filter passband and other ripples, the stopband declines slowly. That is to say, the amplitude-frequency characteristic has the worst frequency selection characteristic. However, the Bessel filter has the best linear phase characteristics. In addition, there is an elliptical filter. The elliptical filter has a ripple in the passband (the stopband is flat or equal ripple), and the stopband drops the fastest. Car Accessories,car audio player,car MP3 player,car FM transmitter Jiangmen soundrace electronics and technology co.,ltd. , https://www.soundracegroup.com