Relationship between active power and reactive power of R, L, and C components - News - Global IC Trade Starts Here.
1. A resistor only consumes power and does not generate it.
2. An inductor does not consume real power. However, it absorbs reactive power since QL > 0.
3. A capacitor also does not consume real power. Instead, it produces reactive power, as QC < 0.
Understanding the behavior of resistors, inductors, and capacitors is essential for analyzing AC circuits. While resistors dissipate energy in the form of heat, inductors and capacitors store and release energy in magnetic and electric fields, respectively. This distinction helps engineers design efficient and stable electrical systems, ensuring proper power factor correction and minimizing energy losses.
Automotive relay, relay accessories, relay maintenance, relay wholesale YIWU JINGHONG AUTO PARTS CO.,LTD , https://en.jhauto.ru
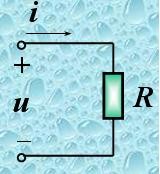
PR = UIcosφ = UIcos0° = UI = I²R = U²/R
QR = UIsinφ = UIsin0° = 0
In a resistive circuit, the voltage and current are in phase, so the reactive power Q equals zero. This means that the resistor only absorbs (consumes) real power and does not produce any reactive power.
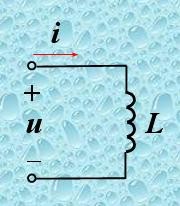
PL = UIcosφ = UIcos90° = 0
QL = UIsinφ = UIsin90° = UI
In an inductive circuit, the voltage leads the current by 90 degrees. As a result, the real power PL is zero, meaning the inductor doesn't consume actual power. However, it absorbs reactive power.
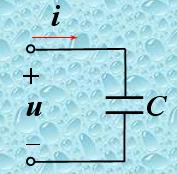
PC = UIcosφ = Uicos(-90°) = 0
QC = UIsinφ = UIsin(-90°) = -UI
In a capacitive circuit, the current leads the voltage by 90 degrees. Therefore, the real power PC is zero, indicating that the capacitor does not consume actual power. However, it provides reactive power to the system.