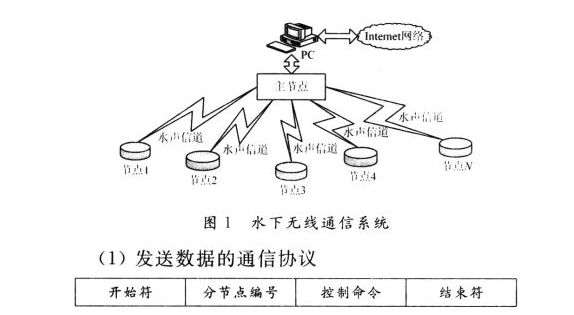
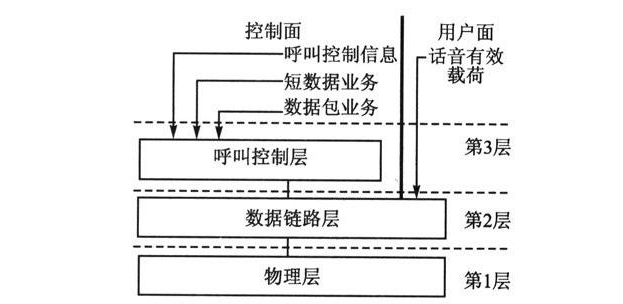
Introduction to data communication protocols _What are the data communication protocols?
Data communication protocol, also known as data communication control protocol. It is a series of conventions prescribed to ensure effective and reliable communication between the two parties in the data communication network. These conventions include the format, order and rate of data, confirmation or rejection of data transmission, error detection, retransmission control and interrogation. There are two types of data communication protocols: one is called basic communication control protocol, which is used for data transmission based on characters, such as BSC protocol (binary synchronous synchronous communication protocol); the other is called advanced key control protocol. Used for bit-based data transmission, such as HDLC (Advanced Data Link Control Protocol) and SDLC (Synchronous Data Key Control Protocol). A data communication protocol is a rule and various stipulations that must be followed between communication objects in a data communication system that can communicate accurately and efficiently. Data communication is a new type of communication after telegraph and telephone communication. It is a combination of computer technology and communication technology. Telegraph communication and telephone communication are human-to-human communication, and communication control functions such as rate control in the communication process are performed by humans. Data communication is mainly between human-machine or machine-to-machine communication. The term "machine" as used herein refers to an electronic computer. Its communication control function can only be strictly in accordance with what is set in the computer in advance, such as "what kind of procedure is used." , exchange of information in any format, etc. rules and various agreed matters. The basic protocol is used in a simple low-speed communication system, the transmission speed is generally not more than 9600 bps, and the communication is asynchronous/synchronous half-duplex mode. The error control is the policy code check. The advanced key control protocol adopts a unified frame format with high reliability, high efficiency and high transparency, and is widely used in public data networks and computer networks. The transmission rate is generally 2.4 kbps to 64 kbps, the communication is continuously transmitted in a synchronous full-duplex mode, and the error control is a cyclic redundancy code check. In fact, communication protocols are generally divided into several levels that are independent of each other. According to the ISO OSI seven-layer reference model, the data communication protocol of the utility data network mainly involves the first three layers, namely the physical layer. Data key layer and network layer. For example, popular packet-switched networks often use the X.25 protocol proposed by CCITT as a fundamental part of the communication protocol. Data communication protocols have two distinct features. First, they all adopt a hierarchical structure. A network architecture is actually a collection of communication functional layers and protocols. In an open system, each end system must implement a seven-layer protocol in the open system interconnection reference model, and the relay system executes its lower three-layer protocol. Second, data communication protocols are all in the form of standards. The standards mentioned here include international standards and standards of companies from various countries. The international standards for data communication protocols mainly include relevant CCITT recommendations and ISO standards. The CCITT proposal is based on the data communication network. The ISO standard is based on the network terminal system, and the corresponding protocol standards of the two are compatible with each other. CCITT's main recommendations for data communication protocols are V-series recommendations, X-series recommendations, T-series recommendations, and I-series recommendations. The V-series recommendations specify the data transmission protocol in the telephone network (X-series recommendations systematically specify data communication network services and service functions, network architecture, network interconnection, mobile data communication, network numbering scheme, data transmission quality, Protocols such as network management and security architecture, and application protocols such as message processing systems and directory queries; the T-series recommendations specify data communication protocols for data communication in the Integrated Services Digital (ISDN). Different workstations in the network can transmit data between servers, which is due to the existence of protocols. With the development of the network, different developers have developed different communication methods. In order for communication to be successful and reliable, all hosts on the network must be in the same language and cannot have dialects. It is therefore necessary to develop a strict standard to define each bit in each word in each packet between the hosts. These standards come from the efforts of many organizations, agreeing on a common means of communication, namely the agreement. These all make communication easier. Many protocols have been developed, but only a few have been retained. There are many reasons for the elimination of those agreements - poor design, poor implementation or lack of support. And those agreements that have survived have stood the test of time and become an effective means of communication. The three most common protocols in today's LANs are MICROSOFT's NETBEUI, NOVELL's IPX/SPX, and cross-platform TCP/IP. One: NETBEUI NETBEUI is a non-routing protocol developed for IBM to carry NETBIOS communications. NETBEUI lacks routing and network layer addressing, which is both its greatest advantage and its biggest drawback. Because it does not require additional network addresses and network layer headers, it is fast and efficient and works for small workgroup environments where only a single network or the entire environment is bridged. Because routing is not supported, NETBEUI will never be the primary protocol for enterprise networks. The only address in the NETBEUI frame is the data link layer media access control (MAC) address, which identifies the network card but does not identify the network. The router forwards the frame to the final destination by the network address, and the NETBEUI frame completely lacks this information. The bridge is responsible for forwarding communications between networks in accordance with the data link layer address, but has a number of disadvantages. Because all broadcast communications must be forwarded to each network, the scalability of the bridge is not good. NETBEUI specifically includes the counting of broadcast communications and relies on it to resolve naming conflicts. In general, bridging NETBEUI networks rarely exceed 100 hosts. Networks that rely on Layer 2 switches have become more common in recent years. A full conversion environment reduces network utilization, although the broadcast is still forwarded to every host in the network. In fact, the combined use of 100-BASE-T Ethernet allows the conversion of NetBIOS networks to 350 hosts in order to avoid broadcast communication becoming a serious problem. Two: IPX/SPX IPX is a protocol group used by NOVELL for NETWARE clients/servers to avoid the weaknesses of NETBEUI. However, it brings new and different weaknesses. IPX has full routing capabilities for large enterprise networks. It includes a 32-bit network address that allows for many routing networks in a single environment. The scalability of IPX is limited by its high-level broadcast communications and high overhead. The Service AdverTIsing Protocol (SAP) limits the number of hosts in a routed network to several thousand. Although SAP's limitations have been overcome by intelligent router and server configurations, administrators of large-scale IPX networks are still very difficult to work with. Three: TCP / IP Each network protocol has its own advantages, but only TCP/IP allows a full connection to the Internet. TCP/IP was developed by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and some commercial organizations for the US Department of Defense in the 1960s. Even if a nuclear attack destroys most of the network, TCP/IP can maintain effective communication. ARPANET was developed based on protocols and evolved into the Internet as a medium for communication between scientists and engineers. TCP/IP also has the need for scalability and reliability. Unfortunately, speed and efficiency are sacrificed (but: TCP/IP development is funded by the government). After the Internet became public, people began to discover the powerful features of the global network. The universality of the Internet is why TCP/IP is still in use today. Often, without realizing it, users install the TCP/IP stack on their own PCs, making the network protocol the most widely used in the world. The 32-bit addressing scheme of TCP/IP is not sufficient to support the number of hosts and networks that will join the Internet. Thus the standard that may replace the current implementation is IPv6.
Germany type 16A 250V~, IP20, Class I, non-rewirable, single-way socket outlet complies ,with shutter, with a non-rewirable plug, with cord H05VV-F 3G1,0-1,5mm 2 (max length be 2m for 1,0mm 2 and 30m for 1,5mm2 ).
16A 250V~, IP20, Class II, non-rewirable, with single way socket-outlet with shutter, with a non-rewirable plug, with flexible cord H05VV-F (with or without fabric braided cover) 2G1,0-1,5mm 2 (Max. 2m for 1,0mm 2 in length and Max.30m for 1,5mm 2 ). Germany Extension Cord,Power Strip Extension Cord,European Extension,Eu European Power Extension Cord CIXI KYFEN ELECTRONICS CO.,LTD, , https://www.kyfengroup.com