These iders that select high-speed high-frequency test cables are taken away, don't be too touched.
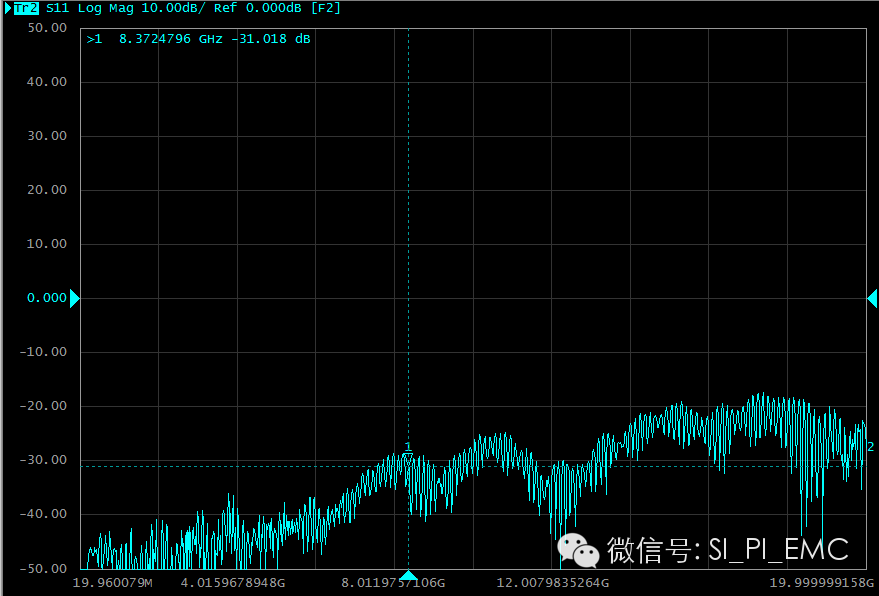
     Before I talk about how to choose a high-speed high-frequency coaxial test cable, let me talk about one thing I have been doing recently, because this thing prompted me to talk about this topic that many people have talked about. Recently, I have been researching a bus that is relatively unfamiliar to everyone. It is a bus protocol jointly developed by Intel and Apple---Thunderbolt . The Chinese name is "Thunderbolt". At present, its third-generation products have also begun to appear. It has reached 40Gbps , so Thunderbolt 's design requirements are relatively high. Intel and Apple require that the bus protocol and interface of thunderbolt be used. Authorization must be authorized. A very important part of the authorization test is the return loss test. And the entire active link is required for return loss testing, which is very challenging for most people. Test cables are required for testing. From the used test fixtures, each cable used is different. Intel uses SMP connectors. Wilder uses 2.94mm heads. Let's do fixtures. Using a 3.5mm connector, this led us to use different test cables to connect to the test equipment. With so many cables, we were very confused. I believe many engineers have similar confusion, so today I will share an article related to the selection of test cables. Here are a few high-speed test coaxial cables and 4 cables that are taken at the lab table . They belong to different companies, including domestic cables (very proud), and cables from international companies. See for yourself if you know which company?). Generally speaking, everyone thinks that the cable is relatively simple. It is a copper wire plus a woven mesh, and then a plastic bag is used. The two ends are connected with the connector. It is usually said that "there is no pain in standing and talking." Children's shoes are spoken. After reading the following, you will know how much a cable needs to pay attention to. The following are the relevant parameters extracted from the article of the professional high-speed high-frequency cable company: Characteristic impedance Standing wave ratio ( VSWR ) and impedance consistency loss rated power Operating voltage Shielding capacitance Transmission rate Cut-off frequency Impulse response Own cable noise range of working temperature Softness Environmental tolerance Cable strength Qualification & UL Certification Look at this and you will know how complicated this cable is. In fact, for our general hardware developers, we pay more attention to the parameters related to cable electrical performance, such as characteristic impedance, standing wave ratio ( VSWR ), impedance consistency, loss, transmission rate, cutoff frequency, shielding. . Characteristic impedance The high-speed high-frequency cables typically have a characteristic impedance of 50 ohms , as well as other special-purpose cables, such as 75 ohm cable and video cables. Cable impedance VSWR and impedance consistency The VSWR reaction is the problem of consistency. In high-speed signal integrity, we usually use the reflection coefficient. The standing wave ratio of the cable is generally very small, and the high-speed high-frequency cable is generally within 1.05 . Standing wave ratio It must be noted that the actual input impedance at a particular frequency may be quite different from the characteristic impedance of the point wave due to the presence of reflection. The voltage standing wave ratio of a specific length point wave means the difference between the actual input impedance of the cable and the average characteristic impedance. loss Attenuation, or attenuation, is an indicator of the energy attenuation as the signal increases in length and frequency. This loss is mainly determined by the conductivity and dielectric loss. In general, the larger the cable, the smaller the conductor loss and the smaller the loss. However, the dielectric loss is independent of the size of the cable, and the dielectric loss plays a major role at high speed and high frequency. In the loss, there is another point that needs everyone's attention, that is, a stability of loss. This stability is not to say that the loss is always constant, but that the loss needs to remain constant at a certain frequency point. In general, cables with a layered structure will have losses that increase with time or number of bends. Therefore, we usually ask the supplier whether the cable is stable or stable when buying the cable, in order to prevent the fluctuations and changes in the value during the test. Cable return loss Transmission rate         The transmission rate of high-speed high-frequency cables is mainly determined by the dielectric constant of the insulating material between the inner and outer conductors. This is the same as the signal propagation rate on the PCB that is well known . This is different from the transmission rate of the signal. Shielding The shielding of the cable mainly means that its signal is not subject to external interference, and the signal is not allowed to interfere with the outside world. We also call the shielding of the cable as isolation. Cut-off frequency A common understanding is that the cable can be at the highest bandwidth frequency without affecting signal transmission. Softness Although this has not much to do with electrical performance, it is still necessary to talk about this. Softness is very important for our testing, because if the cable is too hard, it will make our test system not easy to stabilize, and it will easily damage the test fixture. But the high-speed cables that are currently seen are not very soft. Other parameters not explained here are not important to our high-speed high-frequency, such as environmental tolerance and working temperature. This is very important when we need to perform high and low temperature tests, if the cable is at 80 °C. When the form changes, it will completely change our test results. In short, the choice of high frequency and high frequency test cables must be met: not let our test results be affected by the cable. This is actually what we need to guarantee when building a test system. Nano blackboard is a high-tech interactive teaching equipment, using the world's leading nano touch technology, it can seamlessly switch between the traditional teaching blackboard and the intelligent electronic blackboard through touch, and the teaching content can also be carried out when writing with chalk. Synchronous overlay interaction. The traditional blackboard is turned into a perceptible interactive blackboard, which has achieved an innovative breakthrough in interactive teaching.Smart Nano blackboard also has a Interactive Whiteboard function, 20 electric touch functions can be realized through capacitive touch technology, and writing on the blackboard can be done by fingers. Nano blackboard is a feature-rich multimedia teaching device. blackboard,smart blackboard,interactive blackboard,nano blackboard,intelligent blackboard Jumei Video(Shenzhen)Co.,Ltd , https://www.jmsxdisplay.com

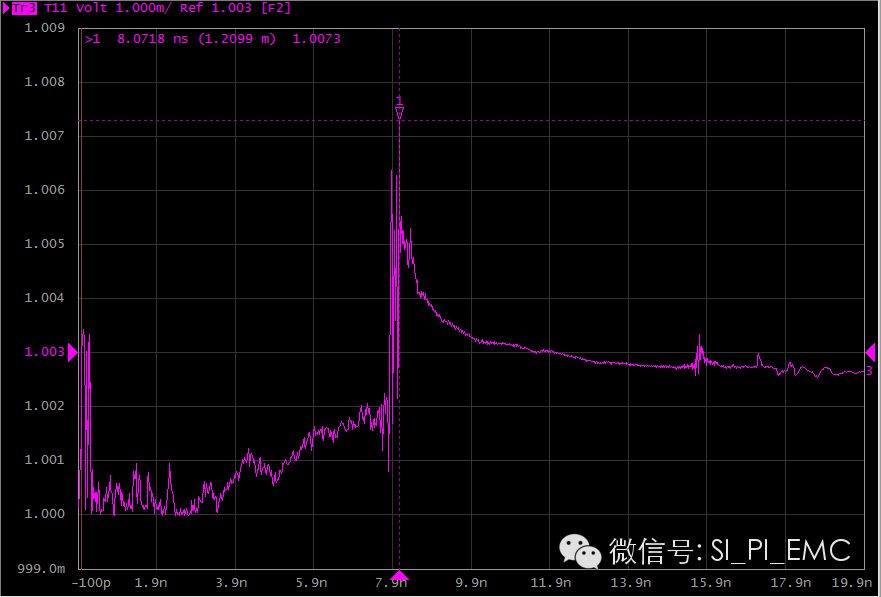
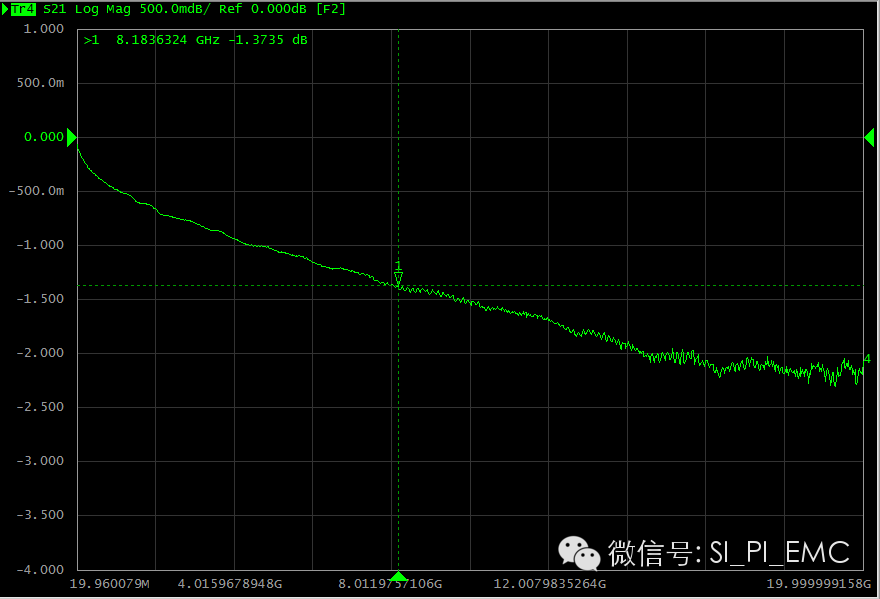 Cable insertion loss
Cable insertion loss