Professional terms speaker, speaker, crossover, power amplifier
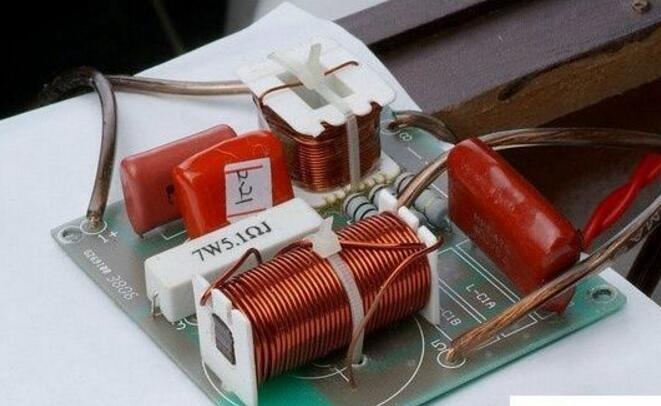
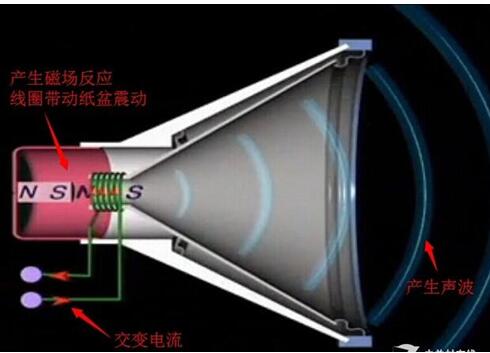
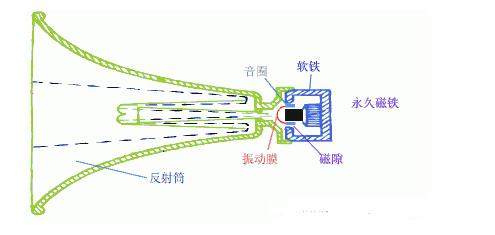
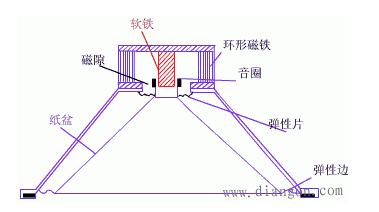
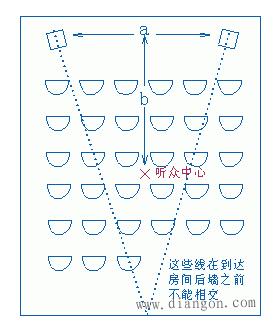
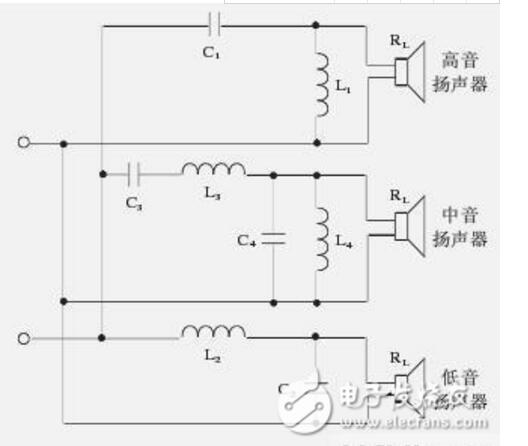
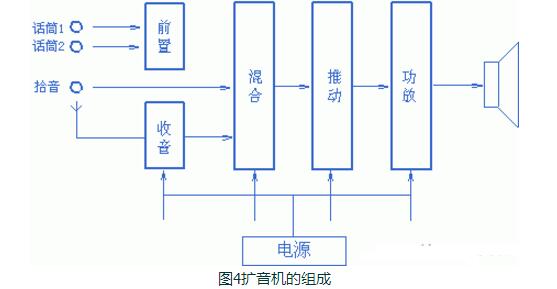
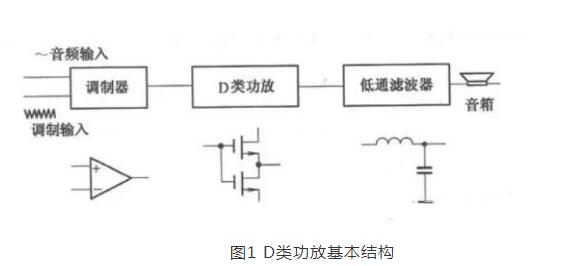
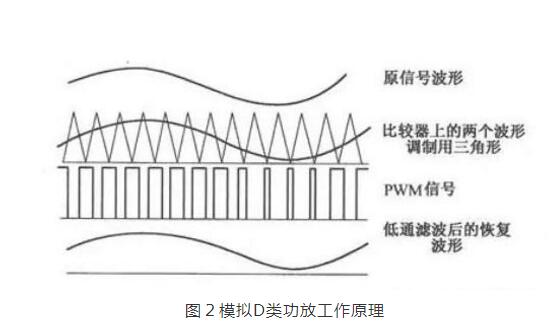
This article mainly explains the speakers, speakers, crossovers, and power amplifiers. First, the composition, principles, classification, and performance indicators of the speakers are introduced. Second, the principles and use of speakers are introduced. Finally, the principles and methods of crossovers, power amplifiers, and power amplifiers are detailed. The role, specifically follow the editor to understand. A speaker refers to a device that can convert audio signals into sound. Generally speaking, it refers to the power amplifier provided in the main body of the speaker box or the subwoofer box. After the audio signal is amplified, the sound is played back by the speaker itself to make the sound louder. The sound box is the terminal of the entire sound system. Its function is to convert the audio electrical energy into corresponding sound energy and radiate it to the space. It is an extremely important part of the sound system, and is responsible for converting electrical signals into acoustic signals for human ears to listen directly. The composition of the speaker There are all kinds of speakers on the market, but no matter which one is composed of the two most basic parts of the speaker unit (the term speaker unit) and the cabinet, in addition, most speakers use at least two or more The speaker unit implements the so-called multi-channel audio reproduction, so the frequency divider is also an indispensable part. Of course, there may be other components in the speaker, such as sound-absorbing cotton, inverted tubes, folded "labyrinth pipes", ribs / reinforced partitions, but these components are not essential for any speaker. The most basic composition of the speaker The element has only three parts: the speaker unit, cabinet and crossover. The principle of speaker sound To understand the principle of sound produced by the speaker, we first need to understand the propagation of sound. The propagation of sound requires a medium (vacuum cannot transmit sound); the sound must rely on all gases, liquids, and solids to spread out as a medium. These substances as a medium of transmission are called media. Just like a water wave, you throw a stone on the calm water, and there is a wave on the water surface, and then propagate to the other side for 4 weeks; the sound wave is also formed in this way. The frequency of the sound wave is in the range of 20-20,000 Hz, and can be heard by the human ear; below or above this range, the human ear cannot hear. Water waves and sound waves propagate in the same way. Only through the propagation of the medium can the human ear hear the sound Sound waves can propagate in gases, solids, and liquids Let me talk about the working principle of the speaker. A horn is a device that converts electrical signals into acoustic signals. It consists of coils, magnets, paper cones, etc. The current (alternating current) of different sizes output by the amplifier moves the coil under the action of the magnetic field through the coil. The coil is connected to the paper cone to drive the paper cone to vibrate, and then the vibration of the paper cone pushes the air to make a sound. The sound principle of the horn When the speaker receives the electrical signal output by the sound source device, the current will pass through the coil on the speaker and generate a magnetic field reaction. The current through the coil is an alternating current, and its positive and negative poles are constantly changing; the positive and negative poles will attract each other, and the coil will be attracted by the magnet on the horn to move backward (in the box); the positive pole and the positive pole will repel each other. , The coil moves outward (outside the box). This expanded rhythm will produce sound waves and air currents, and emit sound, which has the same effect as the throat vibration of our speech. The classification of speakers The classification of speakers has different angles and standards. According to the acoustic structure of the speakers, there are closed boxes, inverted boxes (also called low-frequency reflection boxes), passive radiator speakers, and transmission line speakers. For their respective characteristics, see details. Related question and answer. Inverted boxes are the current mainstream in the market; judging from the size and placement of speakers, there are floor boxes and bookshelf boxes. The former is relatively bulky and is generally placed directly on the ground, and sometimes shock-absorbing feet are also installed under the speakers. nail. Due to the large volume of the cabinet and the convenience of using larger and more bass units, the floor box is usually better at low frequencies, and has a higher output sound pressure level and strong power carrying capacity, so it is suitable for larger listening areas or more comprehensive requirements. Use in occasions. The bookshelf box is small and usually placed on a tripod. It is characterized by flexible placement and does not occupy space. However, due to the volume of the box and the size and number of the woofer, its low frequency is usually not as good as the floor box, carrying power and output sound pressure. The level is also smaller, suitable for use in smaller listening environments; it is divided according to the narrow bandwidth of the playback, there are wideband speakers and narrowband speakers, most speakers are designed to cover the widest possible frequency band , Belonging to a wide-band speaker. The most common narrow-band speakers are the subwoofers (subwoofers) that have emerged with home theaters. They are only used to restore a very low frequency range from ultra-low frequency to low frequency; according to the presence or absence of a built-in power amplifier, they can be divided into passive speakers and For active speakers, the former has no built-in power amplifier and the latter has. Most current home speakers are passive, but subwoofers are usually active. Speaker performance indicators General speakers are marked with many of his application parameters. The most common ones are: Power: generally measured by W or VA, the common is the nominal power [rated power, undistorted power] refers to the maximum input power under the condition that the nonlinear distortion does not exceed the standard range of the speaker. He is the normal working power of the speaker, and continuous working for a long time will not damage it. Sensitivity: His definition is the sound pressure generated when a 1 watt power pink noise voltage is applied to the speaker at a meter away from the reference point. Expressed in decibels [db]. The higher the sensitivity of the speaker, the louder it is at the same driving power. This is very important when using a small power amplifier. Impedance: It refers to the audio signal added to the speaker input, the speaker presents a pure resistance. The common ones are 4 Euro, 8 Euro, and there are also 3 Euro and 5 Euro systems abroad. Pay attention to match the output impedance of the power amplifier when using. In particular, the matching of the amplifier to the speaker impedance is particularly important. The speaker is also called "speaker". It is a very commonly used electroacoustic transducing device, and it can be seen in sounding electronic and electrical equipment. 1. The principle of the speaker A speaker is a device that converts electrical energy (output from an amplifier) ​​into sound (mechanical energy). According to different structures, speakers can be divided into electric type, electromagnetic type, piezoelectric type, etc., the most commonly used in audio-visual education is the electric type speaker. (1) Electric Horn Speaker The electric horn speaker is also called a tweeter, and its structure is shown in Figure 1. It is mainly composed of magnetic circuit system, vibration system and sound tube. The magnetic circuit system and the vibration system are installed together, called the pronunciation head. The pronunciation head and the auxiliary sounds can be separated into one. The magnetic circuit system is composed of permanent magnets and soft iron, and the magnetic field is concentrated at the gap. The vibration system consists of a diaphragm with a voice coil, which is located in the middle of the magnetic gap. When the audio current passes through the voice coil, the magnetic coil forces the voice coil to move the diaphragm forward and backward, causing the air to vibrate. Because the helper Jane is installed in front of the pronunciation head, it can resonate the air and make a loud sound. "? xml: namespace prefix = o ns = "urn: schemas-microsoft-com: office: office" /》 Figure 1 Electric Horn Speaker (2) Electric cone speaker Electric cone speaker is also called woofer, its structure is shown in Figure 2. It is mainly composed of magnetic circuit system and vibration system. The magnetic circuit system consists of a ring-shaped permanent magnet and soft iron, and the magnetic field is concentrated at the gap. The vibration system consists of a paper cone with a voice coil, and the elastic sheet fixes the voice coil in the center of the magnetic gap. When an audio current passes, the voice coil moves forward and backward with the paper cone under the action of the magnetic field, thereby making a sound. Figure 2 Electric cone speaker (3) Combined speakers In order to improve the sound quality and expand the effective frequency range, usually several speakers with different frequency response ranges are combined together and put into the same auxiliary speaker to form a combined speaker. It can significantly improve the frequency response curve in the entire audio range. 2. Use of speakers (1) Select the type of speaker correctly. For outdoor use, electric horn speakers should be used; for indoor use, electric cone-type field speakers should be used, and helper boxes should be selected; when high-fidelity sounds are required to be restored, high-quality combination speakers should be used. (2) The power obtained by the speaker in the circuit should not exceed its rated power, otherwise it will burn the voice coil or dissipate the voice coil. (3) Note that the impedance of the speaker should match the output impedance of the amplifier to avoid damage to the speaker or the amplifier. (4) When using electric horn speakers, you must put the pronunciation head on the sound tube and then power on, otherwise it will be easy to damage the pronunciation head. (5) When using more than two speakers together, attention must be paid to the phase problem. If reversed, the sound will be significantly weakened. When setting up stereo speakers, pay more attention to the wrong phase. (6) When using a stereo playback system, the two speakers should be separated by an appropriate distance, as shown in Figure 3. According to experience, the distance between the two speakers should be equal to the length of the speaker to the middle of the listener. Figure 3 layout of stereo speakers The frequency divider is actually a small part in the speaker, and it is also a very important part. Although the frequency divider is unremarkable, its role cannot be ignored. When the speaker plays sound, it needs to be processed by the frequency divider It can only be released. The current frequency divider is mainly composed of two types, one is an analog frequency divider, and the other is a digital frequency divider. In the ordinary people's understanding, the frequency divider is actually the brain of the speaker, and it cannot be missing. Principle of frequency divider From the circuit structure point of view, the crossover is essentially an LC filter network composed of capacitors and inductors. The treble channel is a high-pass filter, which only passes high-frequency signals and blocks low-frequency signals; the opposite is true for the bass channel. The bass passes to block high-frequency signals; the mid-range channel is a band-pass filter. Except for the frequency between the low and high two crossover points, both high-frequency and low-frequency components will be blocked. In the actual frequency divider, in order to balance the sensitivity difference between the high and low units, attenuation resistors are also added; in addition, some frequency dividers also include an impedance compensation network composed of resistors and capacitors, the purpose of which is to Make the impedance curve of the speaker psychologically flat, so that the amplifier can be driven. Since the current speakers almost all adopt the design method of multi-unit sub-band playback, there must be a device that can divide the full-band music signal sent by the power amplifier into treble, bass output or treble, midrange, and bass output as needed. In order to connect with the corresponding speaker unit, the crossover is such a device. If the full-band signal is directly sent to the high, middle and bass units without distribution, the part of the "excess signal" outside the frequency response range of the unit will adversely affect the signal restoration in the normal frequency band, and may even cause The treble and midrange units are damaged. The role of the divider 1. Basic frequency division No matter what type of electronic crossover the main functions and tasks are of course frequency division. Because there are many kinds of speakers now, what kind of function and function should be used in the system, and the electronic frequency divider of a few frequency division still needs to be flexibly configured. The electronic frequency divider that is usually used now has frequency division 2, frequency division 3, frequency division 4 Equal distinction, more than 4 frequency division is too complicated and meaningless. The frequency divider can reasonably distribute the power of each unit, so that each unit has an appropriate phase relationship to reduce the acoustic interference distortion of each unit during operation. 2. Protect the speakers We know that the working frequency of different speakers is different. Generally speaking, the louder speakers have better low-frequency characteristics and lower frequency dive. The electronic crossover can provide the best working frequency required by different speakers, make up for the sound defects of the unit in a certain frequency band, and make all kinds of speakers work more rationally and safely. Therefore, in addition to the frequency division task, the electronic crossover has more important functions for normal use: protection of speaker equipment. 3. Increase the sound layering If there are many different types of speakers in an audio system, and no electronic crossover is used, there will be many overlapping and repeated parts between the different speakers, and the sound interference will become very serious, and the sound will become It was ambiguous. If an electronic crossover is used in the sound system for reasonable frequency division, the different speakers are in the best working state, so that the frequency range of the sound emitted by different speakers will hardly repeat, and the phenomenon of sound waves interfering with each other is reduced. , The sound will become particularly clear, and the timbre will be better and more layered! Divider classification There are two types of crossovers: one is the passive crossover (PassiVe Crossover), also known as the power divider; the other is the active crossover (Active Crossover), also known as the electronic crossover. 1. Passive crossover Passive frequency divider is a built-in frequency divider of the speaker, which is composed of capacitor and inductance filter network. Its characteristic is that the frequency divider network is set between the power amplifier and the speaker. This frequency divider divides the full frequency audio power signal directly from the power amplifier into bass and treble or bass, midrange and treble, and distributes the frequency-divided signal to the speakers of each frequency band according to different frequency bands. In the full-frequency high-frequency, low-frequency or high-frequency, middle-frequency and low-frequency active frequency division speakers, the passive frequency division circuit completes the frequency division task. The advantages of passive frequency division are: first, the structure is simple, the cost is low, and the sound is installed together, no adjustment is required, and it is convenient to use; second, the system connection is easier, as long as the amplifier is input with a full-frequency signal, the amplifier and the speaker are connected Together, you can achieve full-frequency playback; third, fewer power amplifiers are required. Generally, one power amplifier can bring two full-frequency passive crossover speakers, so the system cost is lower. The disadvantage of passive frequency division is: first, the frequency division network must bear a large amount of power and current added to the speaker, so a larger volume of inductance is used, and because the parameter of the inductance is directly related to the impedance of the speaker, the impedance of the speaker It is also a function of frequency, which deviates greatly from the nominal value, so the error is large and the calculation is difficult; secondly, after the power audio signal output by the power amplifier passes through the capacitor and inductor filter, it will inevitably be due to the nonlinearity of the capacitor and inductor Distortion, sound distortion is inevitable; third, the audio power signal output from the power amplifier will cause a loss of power signal every time through a capacitor and inductance device, so the passive crossover power signal loss is greater; Finally, the frequency division attenuation The rate cannot be made too high, generally up to 12dB / octave, and the interference in the crossover region is too large. This is because the passive divider increases the frequency division attenuation rate by adding capacitors or inductors, that is, the filter order , But increasing the number of capacitors or inductors means increasing signal distortion and power loss, and increasing the crossover attenuation rate The result is more problems. As the name implies, passive frequency division is a kind of "helpless": the frequency division method, the full-frequency power signal output by the power amplifier has to be divided, and without division will cause a series of problems, so it can only be forced to divide the power signal. . In order to reduce the system cost, civilian speakers all adopt passive frequency division. Professional speakers are very different from civilian speakers in terms of requirements, listening subjects, and users. Therefore, in addition to passive crossover speakers, there are also active crossover speakers. 2. Active crossover Active frequency divider is a device that divides the full frequency audio weak signal. It is generally composed of an active electronic circuit frequency division system. Its characteristic is that the frequency division system is located in front of the power amplifier and weakly divides the full frequency audio. Send the bass, treble or bass, midrange and treble signals to their respective power amplifiers, and then output them to the bass, treble or bass, midrange and tweeters respectively by the power amplifier. This method is called active frequency division because it works at In the case of weak signals, low-power electronic active filters can be used to achieve frequency division. Each speaker unit of a passive frequency-divided speaker has its own power signal interface. Some high and low-separated speakers can have both active frequency division and passive frequency division. There are active frequency divisions behind these speakers (AcTIve) and passive crossover (Passive) transfer switches. Some of these speakers are also equipped with a locking mechanism to avoid accidental dialing. When using the active crossover method, be sure to set the crossover mode switch to the "AcTIve" side, connect the treble amplifier to the high (Hi2h) input, and the bass amplifier to the low (Low) input. There are many advantages of active frequency division. First, due to the use of weak signal electronic circuit signals for frequency division processing, the sound signal loss is small, the distortion is small, and the reproduction sound quality is good; second, the frequency division attenuation rate can be made higher than that of passive frequency division. It is easy to reach 24dB / octave. The crossover crossover area is much smaller than the passive crossover. The interference between the high and low sounds in the crossover crossover area is basically overcome. The third is good adjustability. The acoustic index is high. None of the shortcomings of active frequency division is related to sound quality. The main problems are: First, high cost and large investment. Because the active crossover method has high and low frequencies, separate power amplifiers are used for each channel, so many power amplifiers are used. For example, one-to-two distribution speakers need to be driven by two power amplifiers; the second is to add an electronic crossover, which makes the Increase the difficulty of use in connection and adjustment. Power amplifier is referred to as power amplifier, commonly known as "amplifier". It is the most basic equipment in the audio system. Its task is to amplify the weak electrical signal from the signal source (from the mixer in the professional audio system) to drive the speaker to emit sound. . The composition of the power amplifier Power amplifier performance index Output power Output power: The unit is W. Due to the different measurement methods of various manufacturers, there are some different names. For example, rated output power, maximum output power, music output power, peak music output power. Music power Music power: refers to the instantaneous maximum output power of the power amplifier to the music signal under the condition that the output distortion does not exceed the specified value. Peak power Peak power: refers to the maximum music power that the power amplifier can output when the volume of the power amplifier is adjusted to the maximum without distortion. Rated output power Rated output power: The average output power when the degree of harmonic distortion is 10%. Also known as the maximum useful power. Generally speaking, the peak power is greater than the music power, and the music power is greater than the rated power. Generally speaking, the peak power is 5-8 times the rated power. Frequency response Frequency response: indicates the frequency range of the power amplifier and the unevenness within the frequency range. The straightness of the frequency response curve is generally expressed in decibels (db). The frequency response of household HI-FI amplifiers is generally 20Hz--20KHZ plus or minus 1db. The wider the range, the better. The frequency response of some of the best power amplifiers has been achieved 0--100KHZ. Distortion: Distortion: The ideal amplifier should faithfully restore the input signal after it has been amplified. However, due to various reasons, the signal amplified by the power amplifier is often compared with the input signal to produce different degrees of distortion. This distortion is distortion. Expressed as a percentage, the smaller the value, the better. The total distortion of the HI-FI amplifier is between 0.03% and 0.05%. The distortion of the power amplifier includes harmonic distortion, intermodulation distortion, crossover distortion, clipping distortion, transient distortion, transient intermodulation distortion, etc. Signal-to-noise ratio Signal-to-noise ratio: refers to the ratio of the signal level to the various noise levels output by the power amplifier, expressed in db, the larger the value, the better. The signal-to-noise ratio of general household HI-FI amplifiers is above 60db. Output impedance Output impedance: The equivalent internal resistance presented to the speaker is called the output impedance How the power amplifier works The working principle of the power amplifier is actually very simple. It is to amplify various sound signals played by the sound source to promote the sound of the speaker. We use the common working principle of class D amplifier to explain in detail: Class D power amplifier is an amplification mode in which the amplifying element is in the working state of the switch. When there is no signal input, the amplifier is in the cut-off state and does not consume power. During operation, the input signal allows the transistor to enter a saturated state. The transistor is equivalent to an on switch that directly connects the power supply and the load. The ideal transistor does not consume power because there is no saturation voltage drop. In fact, the transistor always has a small saturation voltage drop and consumes part of the power. This power consumption is only related to the characteristics of the tube, and not to the size of the signal output, so it is particularly beneficial for ultra-high power occasions. In an ideal situation, the efficiency of the class D amplifier is 100%, the efficiency of the class B amplifier is 78.5%, and the efficiency of the class A amplifier is only 50% or 25% (depending on the load mode). Class D amplifiers actually only have a switching function. In the early days, they were only used in the switching control circuits of actuators such as relays and motors. However, with the continuous deepening of the research on digital audio technology, the function of switching (that is, the function of generating digital signals) has become increasingly smooth. In the 1960s, designers began to study the amplification technology of Class D amplifiers for audio. In the 1970s, Bose began to produce Class D automotive amplifiers. On the one hand, automotive batteries require higher efficiency, and on the other hand, there is little space to put in a power amplifier with a large heat dissipation plate structure. Both hope to have an efficient amplifier such as Class D to amplify audio signals. The key step is the modulation of the audio signal. Figure 1 shows the basic structure of a Class D amplifier, which can be divided into three parts: The first part is the modulator. The simplest one is to complete the comparator with only one op amp. Put the original audio signal with a certain DC offset and put it on the positive input of the op amp, and generate a triangle wave through the self-oscillation to the negative input of the op amp. When the potential on the positive terminal is higher than the triangle wave potential on the negative terminal, the output of the comparator is high, otherwise the output is low. If the audio input signal is zero and 1/2 of the peak value of the DC offset triangle wave, the high and low levels of the comparator output last the same time, and the output is a square wave with a duty ratio of 1: 1. When there is an audio signal input, during the positive half cycle, the comparator output high level time is longer than the low level, the duty cycle of the square wave is greater than 1: 1; during the negative half cycle, due to the DC bias, the comparator The level of the positive input is still greater than zero, but the time when the amplitude of the audio signal is higher than the amplitude of the triangle wave is greatly reduced, and the duty cycle of the square wave is less than 1: 1. In this way, the waveform output by the comparator is a waveform whose pulse width is amplitude-modulated by the audio signal, which is called PWM (PulseWidthModulaTIon pulse width modulation) or PDM waveform. Audio information is modulated into a pulse waveform. The second part is the class D power amplifier, which is a pulse-controlled high-current switching amplifier that turns the PWM signal output by the comparator into a high-voltage, high-current high-power PWM signal. The maximum power that can be output is determined by the load, the supply voltage, and the current allowed by the transistor. The third part needs to restore the sound information in the high-power PWM waveform. The method is very simple, only need to use a low-pass filter. However, due to the large current at this time, the low-pass filter resistance of the RC structure will consume energy and cannot be used, and an LC low-pass filter must be used. When a pulse with a duty ratio greater than 1: 1 arrives, the charging time of C is greater than the discharge time, and the output level rises; when a narrow pulse arrives, the discharge time is long, and the output level drops, which is consistent with the amplitude change of the original audio signal , So the original audio signal is recovered, see Figure 2. Class D amplifier design considerations are completely different from class AB amplifiers. At this time, the linearity of the power amplifier tube has no meaning, and the more important switch response and saturation voltage drop. Because the pulse frequency processed by the power amplifier tube is dozens of times that of the audio signal, and it is required to maintain good front and back edges of the pulse, the switching response of the tube is better. In addition, the efficiency of the whole machine is entirely due to the pipe consumption caused by the saturation pressure drop of the pipe. Therefore, the small pressure drop of the saturation tube not only has high efficiency, but also the heat dissipation structure of the power amplifier tube can be simplified. A few years ago, the price of such high-frequency high-power tubes was expensive, which limited the development of Class D amplifiers to a certain extent. Now MOSFETs with small current control and large currents have been widely used in the industrial field. Especially in recent years, UHCMOSFETs have been applied to Hi-Fi amplifiers, and the obstacles of the devices have been eliminated. The modulation circuit is also a special link of class D power amplifier. To modulate the audio below 20KHz into a PWM signal, the triangle wave frequency must reach at least 200KHz. If the frequency is too low to meet the same requirements of the THD standard, the components of the passive LC low-pass filter are high and the structure is complex. The frequency is high, the sawtooth of the output waveform is small, which is closer to the original waveform, the THD is small, and the filter can be made with a relatively low value, small size and relatively low inductance and capacitance requirements, and the cost is reduced accordingly. But at this time, the switching loss of the transistor will increase with the increase of frequency. The high-frequency loss in passive devices and the skin effect of Xie frequency will make the efficiency of the whole machine decrease. Radio frequency interference will also occur at higher modulation frequencies, so the modulation frequency cannot be higher than 1MHz. At the same time, the shape of the triangular waveform, the accuracy of the frequency, and the jitter of the clock signal will all affect the distortion of the recovered signal and the original signal. So to achieve high fidelity, many of the same considerations as digital audio fidelity have emerged. Another factor that has a lot to do with sound quality is the passive filter between the drive output and the load. The low-pass filter works under high current, and the load is the speaker. Strictly speaking, the change in speaker impedance should be taken into account in the design, but it is not feasible to specify the speaker as a power amplifier product, so there is a world of enthusiasts in the matching of class D amplifiers and speakers. The role of the power amplifier The role of the power amplifier is to amplify the weak signal from the sound source or pre-amplifier, and promote the speaker to play sound. The function of a good sound system amplifier is indispensable. Amplifier is the largest family of all kinds of audio equipment. Its function is to amplify the weak signal input by the audio equipment and generate enough current to push the speaker to reproduce the sound. Due to the consideration of power, impedance, distortion, dynamics, and different use ranges and control adjustment functions, different power amplifiers have different internal signal processing, circuit design, and production processes. Plug-In Connecting Terminals,Insulated Spade Terminals,Cable Connector Double Spade Terminals,Vinyl-Insulated Locking Spade Terminals Taixing Longyi Terminals Co.,Ltd. , https://www.longyicopperlugs.com