New concept of HFC bidirectional transformation of popular technology
There are many types of two-way access network technologies, which one is in line with NGB positioning and which is the best choice. It is worth discussing that the same technology can only be properly planned and deployed at the physical level to reflect its advantages. HFC two-way transformation popular technology Shenzhen Innovative Cloud Computer Co., Ltd. , https://www.xcycomputer.com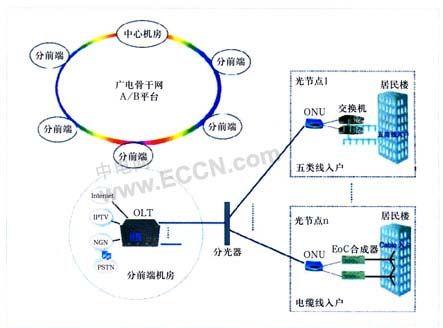
CMTS adopts CMTS for HFC two-way access reconstruction. It does not make any changes to the original line. It only adds or transforms equipment at the node, so the cost is the lowest, but the system broadband support is not enough. The single headend CMTS downlink bandwidth is less than 50M, and the Docsis3.0 version is only 160M, and the technical solution is shared by multiple users, which does not meet the future evolution of NGB's high-performance broadband access requirements;
The FTTB + LAN point-to-multipoint PON passive optical network access technology is similar to the traditional CATV point-to-multipoint multicast method, and tends to be consistent in the network topology. Therefore, when the concept of PON technology is proposed, it is considered to be A networking technology that is very suitable for broadcasting, on-demand, and two-way interaction; FTTB optical fiber entry-to-building photoelectric nodes are located in the building, environmental safety factors are improved, and the failure rate is effectively reduced. The feature of this solution is that the PON and CATV system are independent, that is, the original CATV independence is maintained. When the PON fails, it will not affect the operation of the traditional CATV service. Terminal fusion can be unified or separated on the STB set-top box:
This solution needs to solve two problems. First, the optical path needs to be modified to adapt to the split ratio of the PON system. It can be re-planned throughout the process to provide the corresponding number of fiber cores for each segment of the PON; it can also be taken after the original main optical node. Start PON network planning, which is the current common practice, but the subsequent expansion and extension, such as from FTTC to FTTB / FTTH network planning will become quite complicated, because the later large-scale deployment of FTTH will inevitably increase the demand for front-end backbone optical link resources. At present, the radio and television metro access links are very thin; they can also be changed into place at once, that is, the optical path part is completely transformed by PON networking. This has the advantage that the access network structure is clearer and the original CATV Adopt the wavelength coupling method, and at the same time, the optical link resources occupy the least. This architecture is applicable to E / GPON. It can be smoothly upgraded from the application layer to 10GPON. It is relatively simple to extend from the physical layer to FTTH.
The second problem is the re-laying of Category 5 lines, because the Category 5 lines of general real estate agents are only pre-buried in the user's room, rather than all laying in the building, so the difficulty of transformation has increased. In addition, the adoption of this technical solution for HFC optical copper entry and retrogression should at least be pushed into the building, and CATV and PON system intermediate active nodes should be placed at the same location to reduce the introduction of power and reduce maintenance costs. Therefore, FTTB here refers to CATV Synchronous light with PON enters the building, and the following concepts are the same.
The difference between FTTB (PON) + EOC and FTTB + LAN is that CATV and PON are integrated at the corridor node. EOC (EthernetoverCoaxial) is used to transmit bidirectional IP data while transmitting CATV signals with coaxial cable. Also on the user side, the independence of the CATV system is adopted, and failure of the EOC terminal does not affect the CATV business.
The biggest advantage of this solution is that it minimizes the changes of the original wiring in the building, without the need to re-lay five types of wires, and the traditional CATV coaxial cable can be used. But not all the original structures are suitable for EOC technology. For the buildings in the old area, the coaxial distribution network still needs to be modified or even re-wired, such as changing from a tree to a star-shaped coaxial distribution network.
FTTH uses all-optical PON for high-bandwidth access to carry any business. Compared with FTTB + LAN / EOC, this solution is reflected in the optical link. The integration and separation of IP and CATV networks are completed on both sides of OLT and ONU; FTTH The ONU is placed in the user room, so there is no electricity node from the OLT to the ONU. There is no need to rent any equipment room facilities. The operation and maintenance cost is extremely low, which meets the needs of future access networks and satisfies full-service operation and efficiently supports the loading of emerging services. Need.
Traditional CATV services can still be operated in relatively independent systems. However, when FTTH is deployed, ONU and ONU are tightly integrated with optical coupling receiving and demodulation. Therefore, the power supply at the ONU node must be continuous to ensure uninterrupted CATV services. This is worth discussing.
When deploying FTTH on a large scale, due to the intensive characteristics of our country, the optical splitter must be close to the user side, so the demand for a large number of backbone optical links will increase rapidly; for broadcast and television, the current metro network optical links are thin, Can not meet the future deployment needs of high-performance broadband access network, so the current broadcast and television in the overall planning of the national backbone network, should increase investment in the construction of metro optical networks.